Lux (lx)
Lux is used to measure the amount of light output in a given area. It enables us to measure the total 'amount' of visible light present and the intensity of the illumination on a surface. Lux is measured by a Luxmeter at a certain point.
Dioptre
Diopter is a unit of measurement that refers to the curvature a lens will have. Greater curvature means thicker lenses, greater magnification, and higher diopters.
Central illumination (Ec)
Also commonly referred to as illuminance or light output - describes the maximum illuminance in lux. Ec is the maximum illuminance in the center of the light field.
Light field center
The point in a field (illuminated area) at which the illuminance reaches its maximum Lux intensity.
Illumination field
The illumination field is the area of a uniformly illuminated surface and will be described as the diameter and distance from the light source.
Color and Kelvin rating
Color temperature is a measure and description of how "warm" (yellow) or "cold" (blue) light from a light source is. Color temperatures are usually classified as warm, cold, or daylight and range from 1,000 to 10,000 degrees in Kelvin (K).
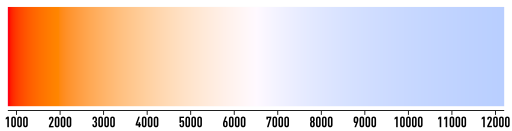
Kelvin value
The low end of the Kelvin (K) spectrum is red, and the high end is blue. Right in the middle is daylight. In essence, the lower the number, the "warmer" or yellower the light, while the higher the number, the "colder" or bluer the light.
Light whiteness is a set of medical conditions of particular importance in physical examination and procedural lighting because physicians, surgeons, veterinarians, and other specialists can very accurately distinguish between the different colors in the body and body fluids required for accurate examination, diagnosis, and treatment.
Warm and cool colors have more yellow, red, blue, and green hues, so can change the way we see color and inhibit accurate diagnosis.
Therefore, medical lighting typically uses a Kelvin range from 5,000 K to 6,500 K, with higher numbers approaching 6,500 K as the light becomes whiter. It is important to note that for longer than 6,500 K, the appearance of the light becomes "cloudy" with the introduction of blue light.
Color
Color rendering is an indication of the ability of a light source to truly reproduce the color of an object.
Color rendering is measured between 0 and 100. This is called the chromogenic index or CRI. Lower values indicate poor color rendering, and then higher values, which is why we often refer to color rendering as accurate color reproduction.
Lumens & Watts
Lumens are 'a unit of luminous flux in the International System of Units, that is equal to the amount of light given through a solid angle by a source of one candela intensity radiating equally In all directions. 'Basically; Lumens = Brightness
Watts measure energy use, not light output. With LED technology, wattage is no longer a reliable method to indicate how bright a bulb is. Instead brightness is expressed as Lumens.
The efficiency of lamps and lanterns
Not all of the light produced by the lamp exits the fixture; some of it stays inside and dissipates as heat. The physical characteristics of the luminaire will affect the amount of light emitted and the amount of light emitted to the working plane.
Most medical lighting users won't be concerned about energy cost efficiency because the lights are only used for a few minutes at a time, but it's crucial to consider the heat generated by the cap.
Lower quality/lower cost surgical lights, lower quality LED technology have higher heat emission around the bulb and into the housing, which heats the housing and makes the lamp too hot to touch, move, etc. Attention therefore needs to be paid to the quality of LED and luminaire head design, i.e. how much of the output is dissipated as heat, which is detrimental to the field of temperature control surgery.